I. Introduction
The interest in AI technologies, particularly computer vision (CV), has skyrocketed in recent years. Companies in manufacturing, supply chain, and logistics are eager to explore AI’s potential to transform their operations. According to Statista, the global market size of the computer vision market is projected to be $45.7 billion by 2028. However, one significant hurdle remains: justifying the investment in AI projects. Many perceive AI as complex and struggle with measuring its return on investment (ROI).
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll introduce a robust framework for identifying opportunities, articulating value, and proving ROI for AI projects. By following this approach, you’ll be well-equipped to champion AI initiatives that leverage cutting-edge technology and deliver measurable business value.
II. Identifying Opportunities for AI Implementation
A. Understanding Your Business Needs
Before diving into AI, it’s essential to conduct a thorough needs assessment. Understanding your business needs will help you identify areas where AI can address specific challenges. Here are some key steps:
- Identify Pain Points: Analyze your current operations to identify pain points and bottlenecks. For instance, in manufacturing, you might face issues with quality control or production delays. In logistics, challenges could include inefficient inventory management or delayed shipments.
- Gather Stakeholder Input: Engage with stakeholders across different departments to gather insights on operational challenges. Listening to the concerns of executives, managers, and frontline employees will provide a holistic view of the issues at hand.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define clear objectives for what you want to achieve with AI. Whether it’s reducing operational costs, improving product quality, or enhancing customer satisfaction, having specific goals will guide your AI implementation strategy.
B. Matching AI Capabilities to Needs
Once you’ve identified your business needs, the next step is to match them with AI capabilities. Different AI technologies offer unique solutions to various challenges. Here’s how to align AI capabilities with your needs:
- Computer Vision for Quality Control: Computer vision can automate visual inspections, ensuring consistent quality control. By identifying defects and anomalies in real-time, CV systems can reduce the risk of defective products reaching customers. According to Deloitte, 93% of companies believe AI will be pivotal in driving growth and innovation in manufacturing.
- Natural Language Processing for Customer Support: NLP can enhance customer support by enabling chatbots to interact with customers, answer queries, and resolve issues efficiently. This reduces the workload on human agents and improves response times.
- Predictive Maintenance with Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms can analyze equipment data to predict maintenance needs. By identifying potential failures before they occur, predictive maintenance can minimize downtime and extend asset life.
C. Conducting Proof-of-Concept Projects
Implementing AI can be a significant investment, so it’s wise to start with proof-of-concept (PoC) projects. PoC projects allow you to test the feasibility and value proposition of AI solutions before full-scale implementation. Here are some benefits of PoC projects:
- Reduced Risk: Starting small with pilot projects reduces the risk of failure. You can evaluate the AI solution’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
- Real-World Data: PoC projects provide the opportunity to gather real-world data, which can be used to refine the AI model and improve its accuracy.
- Stakeholder Buy-In: Successfully demonstrating the value of AI through a PoC project can help gain buy-in from stakeholders and secure funding for larger-scale implementations.
III. Articulating the Value Proposition of AI
A. Focus on Business Outcomes, Not Just Technology
When presenting the value proposition of AI, it’s essential to shift the conversation from the technical capabilities of AI to the tangible benefits for the organization. Here are some key points to emphasize:
- Increased Efficiency: Highlight how AI can streamline operations and reduce inefficiencies. For example, computer vision can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- Improved Quality Control: Explain how AI can enhance quality control by identifying defects and anomalies with higher accuracy than manual inspections. This leads to fewer product recalls and higher customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Quantify the cost savings that AI can deliver. For instance, predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance costs by preventing unexpected equipment failures.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Demonstrate how AI can improve customer experiences. For example, NLP-powered chatbots can provide faster and more accurate responses to customer inquiries.
B. Quantify the Value Proposition with Data
Supporting your claims with data is crucial in articulating the value proposition of AI. Here’s how to effectively use data:
- Historical Data Analysis: Analyze historical data to identify trends and quantify the potential benefits of AI. For instance, if you’re proposing an AI solution for quality control, use historical defect rates to estimate the potential reduction in defects.
- Industry Benchmarks: Compare your current performance with industry benchmarks to highlight areas for improvement. This can help stakeholders understand the potential impact of AI relative to industry standards. For instance, the market size of AI in the manufacturing sector is expected to exceed $2BN by 2025, with an average annual growth of more than 40% from 2019.
- Case Studies: Leverage case studies of similar AI implementations to provide real-world examples of success. This can help build credibility and demonstrate the practical benefits of AI.
C. Tailor the Value Proposition to Different Stakeholders
Different stakeholders have different concerns and priorities. Tailoring the value proposition to address these specific interests is essential for gaining buy-in. Here’s how to approach different stakeholders:
- Executives: Focus on the strategic benefits of AI, such as cost savings, competitive advantage, and long-term growth. Highlight the potential for AI to drive innovation and position the company as a leader in its industry.
- Managers: Emphasize the operational benefits of AI, such as improved efficiency, reduced errors, and streamlined processes. Provide examples of how AI can help managers achieve their departmental goals.
- Operations Teams: Address the practical aspects of AI implementation, such as ease of use, integration with existing systems, and support for daily tasks. Show how AI can make their jobs easier and more efficient.
IV. Proving ROI: Measuring Success with AI
A. Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Defining KPIs is crucial for measuring the success of your AI project. KPIs should align with the value proposition and objectives of the project. Here are some examples of KPIs for AI projects:
- Reduction in Processing Time: Measure how much time is saved by automating tasks with AI. For instance, if you implement computer vision for inventory management, track the reduction in time spent on manual inventory counts.
- Decrease in Error Rate: Monitor the reduction in errors after implementing AI. For example, if you use AI for quality control, track the decrease in defects identified during inspections.
- Increase in Customer Satisfaction Score: Evaluate the impact of AI on customer satisfaction. For instance, if you deploy NLP-powered chatbots for customer support, measure the change in customer satisfaction scores.
B. Establish Baseline Measurements
Before implementing the AI project, establish baseline measurements for the identified KPIs. Baseline measurements provide a point of comparison to evaluate the impact of AI. Here’s how to establish baseline measurements:
- Historical Data Analysis: Use historical data to establish baseline measurements for KPIs. For example, analyze historical processing times, error rates, and customer satisfaction scores.
- Performance Audits: Conduct performance audits to gather current data on key metrics. This can involve manual data collection or the use of existing monitoring systems.
C. Track and Analyze Performance Data
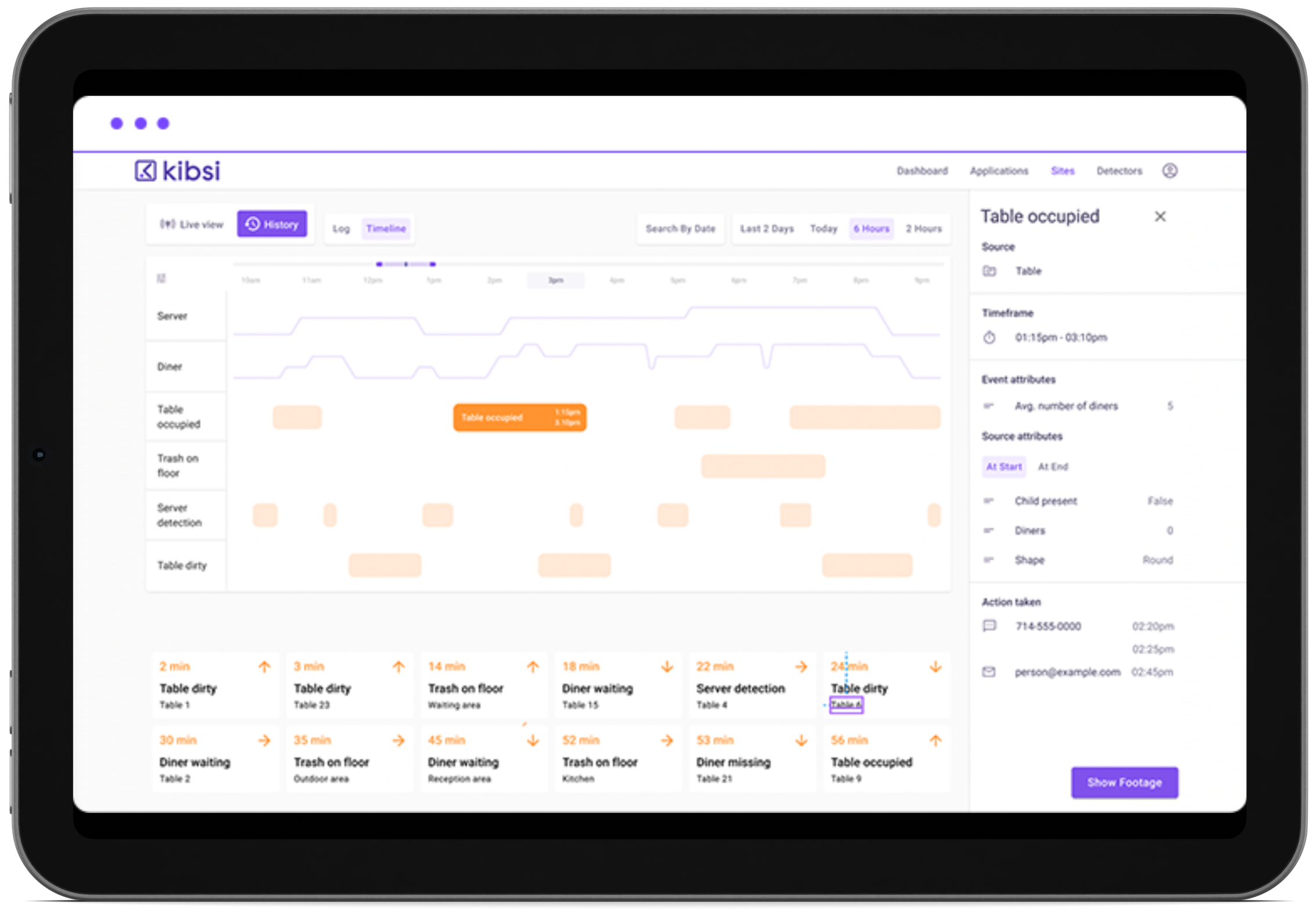
Continuously monitor the identified KPIs to measure the impact of the AI project. Use data visualization tools to track progress and identify areas for improvement. Here’s how to track and analyze performance data:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring systems to track KPIs continuously. This allows you to identify issues and make adjustments promptly.
- Data Visualization: Use data visualization tools to create dashboards and reports that present performance data clearly and concisely. Visualizing data makes it easier to communicate the impact of AI to stakeholders.
- Performance Reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews to analyze the data and evaluate the AI project’s effectiveness. Identify areas where the AI model can be refined and optimized.
D. Calculate and Communicate ROI
Calculating and communicating the ROI of your AI project is essential for demonstrating its value to stakeholders. Here’s how to approach ROI calculation and communication:
- Quantify Benefits: Quantify the benefits achieved through the AI project. This includes cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved quality. Use data from your performance measurements to support your claims.
- Compare Costs and Benefits: Compare the costs of implementing the AI project with the quantified benefits. This includes initial implementation costs, ongoing maintenance costs, and any additional expenses.
- Highlight Short-Term Wins and Long-Term Benefits: Emphasize both short-term wins and long-term benefits. Short-term wins demonstrate immediate value, while long-term benefits highlight the sustained impact of AI on your organization.
- Communicate ROI to Stakeholders: Clearly communicate the ROI to stakeholders through presentations, reports, and meetings. Use data visualization to present key findings and make the information accessible to all stakeholders.
V. Conclusion
Implementing AI in manufacturing, supply chain, and logistics can drive significant business improvements. By following a structured approach to identifying opportunities, articulating value, and proving ROI, you can successfully champion AI projects that deliver measurable value.
Remember, AI is not just about technology—it’s about driving tangible business improvements. By focusing on business outcomes, tailoring your value proposition to stakeholders, and continuously measuring and communicating ROI, you can ensure the success of your AI initiatives. For example, 83% of companies think AI has made or will make a practical and visible impact, with 27% believing AI projects have already brought value to their companies.
VI. Call to Action
At Kibsi, we have been fortunate in helping organizations to identify valuable opportunities for computer vision. Our AI platform is designed to support manufacturing, supply chain, and logistics, providing tailored, vision solutions that drive operational efficiency and innovation.
Interested in discovering more about how computer vision and AI can benefit your organization? We’re here to help. Contact us today to learn more and start your AI journey with Kibsi!